Speed Zones
Table of Contents
The information below is intended to reflect the preferred practice of Main Roads Western Australia ("Main Roads"). Main Roads reserves the right to update this information at any time without notice. If you have any questions or comments please contact Main Roads customer service centre on 138 138 or via the Main Roads website. The Traffic Engineering Standards Manager (TESM) looks after questions or comments relating to this document.
To the extent permitted by law, Main Roads, its employees, agents, authors and contributors are not liable for any loss resulting from any action taken or reliance made by you on the information herein displayed.
1. General
1.1 Introduction
The control of speed is an important aspect in effective traffic management. Speed zoning is used to vary the speed limit of a road or area from that which would otherwise apply under the general limit applicable to the locality. The objective of speed zoning is to provide credible speed limits which meet driver expectations while achieving a balance between road safety, land use, amenity and transport efficiency.
Speed limit signs are regulatory signs and therefore the creation, modification, or removal of any speed zones requires the approval of the Commissioner of Main Roads. The Commissioner has delegated his authority to the Manager Traffic Management Services for approval of speed limits in all areas of Western Australia.
1.2 Scope
The purpose of this document is to provide a uniform approach for implementing and signposting of speed zones for a particular length of road ('linear' speed limits) or a network of roads ('area' speed limits). The policy, application & approval and administration guidelines can be found in the separate document, Speed Zoning - Policy and Application Guidelines.
This document is applicable to all public roads in Western Australia and should also be used by Local Government Authorities (LGAs), State Government departments that may have Authorities created to manage specific locations, such as Kings Park or Rottenest Island, Federal departments that may manage locations such as airports and private authorities for application to non-public roads in the State.
1.3 References
This guideline should be read in conjunction with the following documents, as appropriate:
- Main Roads Speed Zoning: Policy and Application Guidelines
- Main Roads Signs Index
- Main Roads Traffic Control Devices Chapter 3 Sign Standards
- AS 1742 - Series of documents - Manual of Uniform Traffic Control Devices (Parts 1 to 15), and in particular AS 1742.4 (Individual documents are revised over time, which may change or include signs that are not included in AS 1742.1. Therefore all documents relevant to a particular type of traffic control device should be referenced for advice) and AS1742.3 section 3.4 for speed zones within roadworks.
- Austroads – Guide to Road Safety Part 3: – Speed Limits and Speed Management.
- Austroads – Guide to Traffic Management Part 5: – Link Management.
- Austroads – Guide to Traffic Management – Part 8: Local Street Management.
- Austroads – Guide to Road Design – Part 3: Geometric Road Design.
- Road Traffic Code 2000 - Part 3, Speed Restrictions.
- Main Roads Smart Freeways Supplement to Victoria’s Managed Freeway Handbook for Lane Use Management and Variable Speed Limits
- Main Roads Smart Freeways Supplement to Victoria’s Managed Motorway Design Guide Volume 2: Design Practice Parts 2 and 3
1.4 Definitions
SPEED TERMS
Advisory Speed is the desirable speed for comfortable travel for the driver and passengers when weather, traffic and road conditions are good. It is not legally enforceable.
Area Speed Limit means a Regulatory Speed Limit which applies across a specific locality as defined in the Road Traffic Code.
Built-Up Area Speed Limit means the 50 km/h speed limit applicable to a built up area as defined in the Road Traffic Code.
Design Speed means the speed which is adopted for geometric design of either new roadways, or upgrades to existing roadways
Default Speed Limit means the maximum speed limit applicable to a non-speed zoned road as defined in the Road Traffic Code.
Impact Speed means the speed at which a road user or vehicle collides with another object in a crash.
KSI means Killed or Serious Injury
Operating Speed means the speed at which most road users feel comfortable travelling. The operating speed is generally measured as the 85th Percentile Speed. This may be different to the Target Speed.
Posted Speed Limit means the speed zone as indicated by compliant regulatory signage.
Regulatory Speed Limit means a speed limit which can be enforced by the WA Police, including default speed zones, posted speed zones, vehicle type maximum speeds, etc.
Speed Zone means the speed indicated by the numerals on the speed limit sign.
Target Speed means the vehicle speed considered to be in line with the Main Roads Speed Zoning - Policy and Application Guidelines policy, and which should be the basis for setting a regulatory speed, supported by other roadway treatments, where appropriate.
85th Percentile Speed means the speed at or below which 85% of all vehicles are observed to travel under free-flowing conditions past a nominated point.
ROAD FUNCTION TERMS
Access Road means a road provided mainly for access to abutting properties.
Primary Distributor means a road that provides for major regional and inter-regional traffic movement and carries large volumes of generally fast-moving traffic. These roads can be strategic freight routes.
District Distributor A means a road that carries high-capacity traffic movements between industrial, commercial and residential areas and generally connects to Primary Distributor roads.
District Distributor B means a road that has a similar function to a District Distributor A road but with reduced capacity due to flow restrictions caused by frequent property accesses and roadside parking.
Regional Distributor means roads that are not Primary Distributors but which link significant destinations and are designed for efficient movement of people and goods within and beyond regional areas. They are managed by local government.
Local Distributor means a road that caters for movement of traffic within local areas and connects access roads to higher-order distributor roads.
COMMON TERMS
AADT means Annual Average Daily Traffic (the typical number of vehicles traveling along both directions of a road across a 24-hour period).
AS means Australian Standard.
GVM means Gross Vehicle Mass.
ISO means International Standards Organization.
LATM means Local Area Traffic Management.
Main Roads means Main Roads Western Australia.
Managed Freeway means a section of freeway, or control of access highway, that has either on ramp controls to meter traffic or a lane use management system to allow lanes to be shut and traffic directed to other lanes and speed limits to be changed or both
Smart Freeway means Managed Freeway as above.
Road means any highway, road, or street open to, or used by, the public and includes every carriageway, footway, reservation, median strip and traffic island thereon.
Roadway means Road per the above.
Road Traffic Code means Road Traffic Code 2000, regulations for Western Australia applied under the Road Traffic Act 1974.
RTC means abbreviation of Road Traffic Code.
School Zone means a carriageway subject to school zone signage as defined in the Road Traffic Code.
School Frontage Road means any road directly adjacent to any part of a school including playing fields.
Speed Limit Signage means any sign or marking erected or approved by Main Roads to communicate information about regulatory speeds.
Threshold Treatment means a treatment that is placed at a perimeter or entry of a local area to inform motorists that they are entering a different speed environment.
VPD means vehicles per day (typically expressed as the sum of vehicles travelling in both directions for two-way roads).
SAS means Safe Active Street, a term for a street that has had measures installed to encourage active transport.
2. Procedures
Speed limits fall into two main categories:
- Statutory Speed Limits
- Speed Zones
2.1 Statutory Speed Limits
Statutory speed limits are those that, by regulation in the Road Traffic Code, apply to a particular road environment, driving license provision, type of vehicle, or specific location. These speed limits are generally unsigned, with drivers expected to be aware of the limits as part of the process of obtaining and holding a driving license.
Examples of this include heavy vehicle speed limits where a person shall not drive:
- a vehicle towing a trailer or other vehicle at a speed exceeding 100 km/h, or
- a bus with a GVM over 5t at a speed exceeding 100 km/h.
An exception to this is the "WA Maximum Speeds" sign (MR-RS-1), which gives the maximum permissible speed limit in rural (undeveloped) areas for various classes of vehicles.
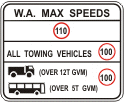
MR-RS-1 |
Sign MR-RS-1 (WA Maximum Speeds) may be used near the boundary of a metropolitan area where the default speed limit changes from 50 to 110 km/h. The sign may also be used on main roads into WA from adjoining states or territories and when leaving airports to highlight the maximum permissible speed in WA. |
Figure 1.
Default speed limits are statutory speed limits applicable to various classes of roads according to their environment. The default speed limits applicable in Western Australia are 50 km/h for built-up areas and 110 km/h for rural or undeveloped areas.
2.2 Speed Zones
“Speed Zones" mean lengths of a carriageway defined at the beginning by means of a speed limit sign, and at the end by means of an END speed limit sign, another speed limit sign or a T-intersection where that carriageway ends.
Speed Zones can be classified as follows:
- Linear Speed Zone – Applied to a length of road.
- Linear speed zones less than 40 km/h;
- Linear speed zones of 50 km/h or higher.
- Area Speed Zone – Applied to a network of roads.
- School Zone – Related to a school and applied to a network of roads.
- Heavy Vehicle Zone.
- Shared Zone – Applied to an area or length of road used by both vehicles and pedestrians with a speed limit of either 10 km/h or 20 km/h.
2.2.1.1. General
a) Length of Speed Zones
The minimum length of posted speed zones should be considered with reference to the time taken to travel the length of the zone at the target speed. The desirable minimum lengths of speed zones are specified in Table 1 and shall be used in place of AS 1742.4 Table 2.1. These minimum lengths typically equate to the distance travelled in 30 seconds at the posted speed limit. However, shorter distances may be acceptable for lower limits on approach to traffic signals, roundabouts, railway crossings, or single lane bridges.
Table 1 – Minimum Lengths of Speed Zones
| Regulatory Speed Limit (km/h) |
Minimum Length of Speed Zone (km) | Typical Travel Time at Regulatory Speed (seconds) |
| 10 | As Appropriate | As Appropriate |
| 20 | As Appropriate | As Appropriate |
| 30 | As Appropriate | As Appropriate |
| 40 | 0.4 | 36 |
| 50 | 0.5 | 36 |
| 60 | 0.6 | 36 |
| 70* | 0.7 | 36 |
| 80* | 0.8 | 36 |
| 90 | 0.9 | 36 |
| 100 | 2.0 | 72 |
| 110 | 4.0 | 131 |
* Traffic Signals speed zoned at 70 km/h (and existing locations that still have the previous maximum speed zone of 80 km/h) are to have a minimum length of 0.3 km. This comprises of 200 m on approach to the intersection and 100 m on departure from the intersection, check section 2.2.1.1 (c) for offset speed limits. Similarly, roundabouts, active railway level crossings, and single lane bridges on a road with a posted speed limit greater than 80 km/h may have short sections of posted speed limits applied on approaches.
b) Speed Zone Transition (formally referred to as Buffer Speed Zones)
A speed zone transition is intended for use where there is a significant reduction, greater than 30 km/h difference, in speed limit along a carriageway. Where there is a significant reduction of the speed limit, normally two speed limit ahead (doubled up) signs (G9-79 size B or C as appropriate) shall be placed in advance of the start of the lower speed zone in accordance with AS 1742.4, Section 3.1.3 (c).
Placement of the speed limit ahead signage may vary to account for adjacent signage, operating speeds, road features, and other hazards. Specifically, the distance travelled at the preceding target speed should also be reviewed to identify the reasonable travel time and distance available for drivers to adjust their speed upon sighting of signage. The visibility of both speed limit ahead and the following speed restriction sign should also be considered, and may justify variation in the location of the placement of speed limit ahead signs to appropriately match road conditions, typically at 4 to 10 seconds of travel time from the change in limit.
For approaches to school zones, where the change in speed zone is 40 km/h or greater or where there is poor horizontal or vertical alignments on approach, sign MR-WDP-6 can be used, see figure 2 below. Speed limit ahead signs (G9-79) are not appropriate on approach to school zones due to the speed zone being time related and not operating at all times.
|
MR-WDP-6 |
School Zone ahead sign for use where the change in speed zone is 40 km/h or greater or where poor horizontal or vertical alignments are present on approach. Speed limit ahead signs (G9-79) are not appropriate due to the speed zone being time related. |
Figure 2
Speed limit ahead signage should not be used for increases in speed limit, or on exit ramps at interchanges, or at approaches and departures to shared zones. Speed limit ahead signage shall only be used for decreases in speed limits as defined in Table 2.
Table 2 – Speed Zone Ahead Signage
| Speed Zone Difference | Speed Zone Ahead Signage |
| 10 km/h | Not to be used |
| 20 km/h to 30 km/h | Optional (site specific) |
| 40 km/h and above | Mandatory (other treatments likely to be required), except at Freeway off ramps and control of access highway off ramps. |
c) Offset Speed Zones
Refer to AS 1742.4, Section 2.2.5, unless otherwise mentioned in this document.
Where offset speed zones are used on divided roads, medians should be continuous over the length of the offset speed zone.
Main Roads does not permit offset speed zones on undivided roads, for permanent installations.
It may be appropriate to use offset speed zones in the following situations:
- On divided roads (including those with a raised median or central barrier), where one direction of a road presents a greater risk to that of the opposing direction (e.g. steep downgrades in combination with poor alignment).
- On divided roads where the roadside development or road geometry on the two sides is markedly different.
- For short transition sections on approaches to intersections or other defined hazards.
- On the departure side of highly localised hazards such as railway crossings or traffic signals.
At steep descents/ascents with barrier lines (double two way or unbroken separation) and climbing lanes for buses and trucks, it may also be desirable for a lower speed limit for descending heavy vehicles only.
d) Road Characteristics
The speed limit based on the appropriate Target speed should reflect the environment that the road is travelling through and not individual isolated hazards or single events that may occur once a year, for example.
Speed limits should not be reduced for isolated road hazards such as un-signalised intersections, driveways and isolated curves. Hazards such as these should be treated with the appropriate warning signs, and where necessary advisory speed signage. However, where several hazards occur in close proximity to each other over a section of road 3 km or more, then a lower speed limit than that indicated by roadside development may be appropriate.
Traffic Signals, where the approach road is speed zoned at 80 km/h or above, the approach shall be a speed zone not greater than 70 km/h with a length not less than 10 seconds travel time of the preceding speed zone, refer table 3.
At Roundabouts, Active Railway Level Crossings and Single Lane Bridges where the approach road is speed zoned at 90 km/h and above, the approach shall be a speed zone not greater than 80 km/h with a length not less than 10 seconds of travel time for the preceding speed zone, refer table 3.
On divided carriageways, if offset speed zones are appropriate, the length of the speed zone should be reduced to 100 m on the departure side of the road feature.
Due to the potential for high severity head-on and head-on evasion crashes at single lane bridges and where a road narrows to a single lane, associated traffic control devices should be provided in addition to normal speed zoning devices (Refer to Main Roads policy on Give Way Control Approaching Narrow Roads and Bridges.)
e) Location of Speed Zone Change
Speed zone changes should occur at a point of clear visual transition along the roadway. Transition points include:
- At the commencement of a roadway/on the departure leg of intersections.
- At a clear change of environment characteristics, such as departure from a shopping area or when entering a residential area from an undeveloped area.
- On approach to a major interchange or intersection.
- Landmarks and/or changes in environment at the entry to a town or urban centre.
- At a change in road seal, road width, road alignment, or other significant geometric feature.
Where speed zone changes occur at or near a major intersection, consideration should be given for placing the transition point in advance of the intersection to reduce the impact speed of potential right angle or rear end collisions that might occur at the intersection. The site conditions on the approach should be evaluated to ensure any relevant factors (such as queueing or sight distance constraints) are considered in the placement of signage.
It is desirable that speed zone changes occur in advance of major intersections to avoid distractions and to allow drivers to adapt to the lower speed limit before reaching the intersection. A typical distance travelled in 4 to 10 seconds at the posted speed is desirable to allow for road users to adjust their travelling speed. Guiding distance values are provided in Table 3 below. Where appropriate conditions exist a distance of 300 m is desirable. However, where the speed zone is lower on the departure side of the intersection (for instance on the terminating leg of a T-junction), the speed zone change should be installed as near as possible to the intersection (100 m in rural areas, 50 m in urban areas) to discourage continuation of the higher travel speeds after the intersection.
Table 3 – Distance Travelled at Posted Speed
| Posted Speed (km/h) |
4 Seconds of travel time (Minimum) |
10 Seconds of travel time (Maximum) |
| 10 | 11 m | 27 m |
| 20 | 22 m | 55 m |
| 30 | 33 m | 84 m |
| 40 | 44 m | 111 m |
| 50 | 55 m | 140 m |
| 60 | 66 m | 166 m |
| 70 | 77 m | 195 m |
| 80 | 88 m | 222 m |
| 90 | 99 m | 250 m |
| 100 | 111 m | 278 m |
| 110 | 122 m | 305 m |
2.2.1.2 Signs
a) General
The signs on linear speed zones are to be installed in accordance with AS 1742.4 Section 3.1.4, other than the following practices which are adopted in Western Australia.
Only the speed restriction sign (R4-1) and the "End Speed Limit" sign (MR-RS-21) should be used for new linear speed zoning applications in Western Australia. Due to size discrepancies between AS1743 and AS1742 the Main Roads “End Speed Limit” sign (MR-RS-21) should be used in preference to the AS1742 and AS1743 “End Speed Limit” sign (R4-12).
The speed restriction sign is used to indicate the speed limit that applies to the speed zone and as a repeater sign. The "End Speed Limit" sign is used at the end of a speed zone or Built-Up Area speed limit and indicates that the default speed limit applies beyond the sign.
The signs to be used at the transition from a sealed to a gravel road are shown in Figure 3.
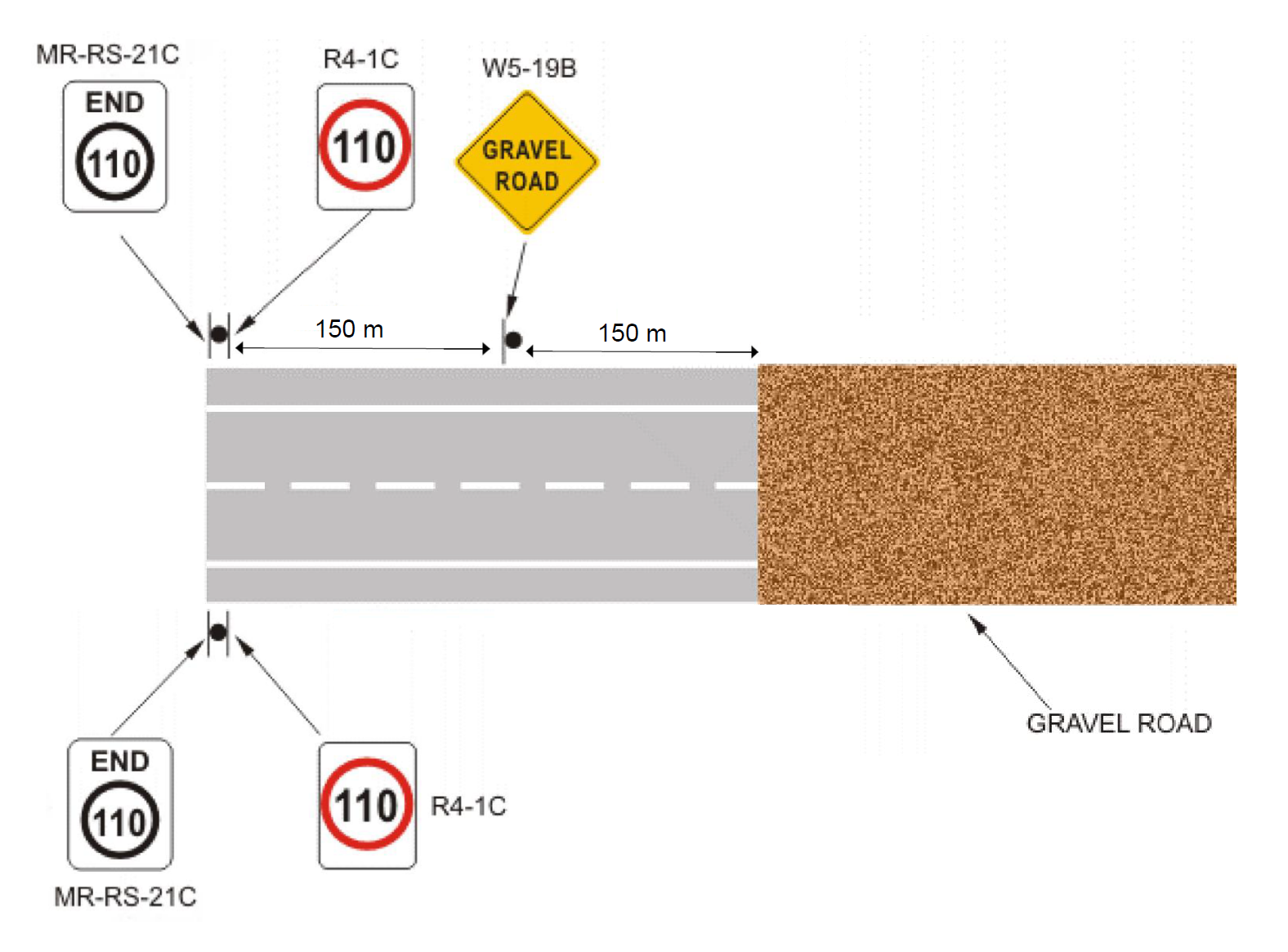
Note: Posted speed and required sign size may vary. Distance between / to signs is approximate.
Figure 3: Signs at the Transition from a Sealed to a Gravel Road
|
MR-RS-21 |
The END Speed Limit sign (MR-RS-21) shall be used at the start point of a continuous section of road covered by the default rural speed limit where it is not practicable or desirable to indicate the speed limit applying beyond the point by means of a Speed Restriction (R4-1) sign. This would be the case where the safe operating speed of the alignment beyond the start point is substantially lower than the default rural speed limit (such as a gravel road) or if there is a hazard such as a busy intersection or railway level crossing just beyond the start of the limit and it is not appropriate to extend the posted speed into this area. |
Figure 4.
b) Speed Limit Signs Used with Other Signs
In general, no other sign should be erected on any post carrying a speed limit sign. The only exceptions are:
- "END OF FREEWAY" (MR-GE-23) and "START OF FREEWAY" (MR-GE-22) supplementary plates, which may be added to the bottom of freeway speed limit signs (refer to section 2.2.1.2 g)).
- "End Speed Limit" sign (MR-RS-21), which shall be erected back-to-back with a speed limit sign, as indicated in Figure 3.
- "End Area Speed Limit" sign (R4-13), which may be erected above a speed limit sign (refer to section 2.2.2.2) to indicate the end of a speed limited area and the start of a linear speed zone.
- "End School Zone" sign (R4-9), which may be erected above a speed limit sign to indicate the end of a school zone and the start of a linear speed zone. If the default urban speed limit of 50 km/h applies after the sign, the "End School Zone" sign shall be installed without a speed limit sign.
- Main Roads School Zone signs (MR-RS-7B, MR-RS-8B, MR-RS-9, MR-RS-14B, MR-RS-15B and MR-RS-16B) – refer section 2.2.3.4.
- "VEHICLES 22.5t GCM OR MORE" (MR-RA-21) supplementary plate is used together with a R4-1 speed limit sign as a repeater sign for Heavy Vehicle Speed Zones as per section 2.2.5.2.
c) Repeater Signs
This section supersedes AS 1742.4 section 3.1.6.
Repeater signs are used:
- To remind drivers of the speed limit.
- To advise drivers where the zoned speed limit might appear inconsistent with surrounding development.
- To advise drivers turning into a speed zoned road from another road or busy intersection, such as a large shopping centre car park.
- To confirm a zone limit after a discontinuity such as a "Y" junction where a road name change occurs.
The location, spacing and number of repeater signs is given in sections 2.2.1.2 e) and 2.2.1.2 f) of these guidelines, respectively.
d) Size of Signs
The sizes of signs used in Western Australia are stated in Tables 4 and 5 of the Sign Standard Guidelines. As a general rule, speed zone change signs are size "C" and repeater signs are size "B". Exceptions to this are:-
- Freeways and Controlled Access Highways - use size "C" signs in both instances.
e) Location and Spacing
(i) Speed Zone Change Signs
As per section 2.2.1.1 d), where the approach road is speed zoned at 80 km/h and above, the approach to a signalised intersection shall be speed zoned not greater than 70 km/h at a distance not less than 10 seconds of travel time for the preceding speed zone, refer Table 3. On approach to a roundabout if the road is speed zoned at 90 km/h or above the approach to the roundabout shall be speed zoned no greater than 80 km/h at a distance not less than 10 seconds of travel time, refer Table 3.
On approach to an Active Rail Crossing if the road is speed zoned at 90 km/h or above the approach to the active rail crossing shall be speed zoned no greater than 80 km/h at a distance not less than 10 seconds of travel time, refer Table 3.
On divided carriageways, if offset speed zones are appropriate, the length of the speed zone should be reduced to 100 metres on the departure side of the road feature.
(ii) Repeater Signs in Urban Areas subject to Built-up Area Speed Limit
In urban areas subject to the built-up area speed limit, where signage is installed that creates a speed limit different to the built-up area default speed limit, repeater signs should be provided at intervals of approximately 1.0 km or on the departure side of major intersections as follows:
- Downstream of an intersection on a terminating leg: 50 – 100 m
- Downstream of an intersection on a continuing leg: 100 – 200 m
It should be noted that it is not Main Roads practice to install speed limit signs on roads subject to the built-up area default speed limit.
(iii) Advisory Repeater Signs on 50 km/h roads that meet the Built-Up Area definition
Advisory repeater signs, “Remember 50 in Built-Up Areas” (MR-WM-57) can be installed where requirements have been met as described in section 5 of the Speed Zoning - Policy and Application Guidelines. This sign replaces the previous practice of installing a 50 km/h repeater sign in exceptional circumstances or if the environment of the road could cause confusion to road users as to whether the Built-Up Area definition had been met. Refer to Figure 22 within section 2.2.6.1.
(iv) Repeater Signs in Urban Areas not subject to the built-up area speed limit
In urban areas not subject to the built-up area speed limit, repeater signs shall generally be located at the intervals given in Table 4, or on the departure side of major intersections as follows:
- Downstream of an intersection on a terminating leg: 50 – 100 m
- Downstream of an intersection on a continuing leg: 100 – 200 m
Repeater signs may also be required where roadside development alters markedly without a change in speed zone.
Table 4 – Maximum Spacing of Repeater Signs for Urban / Outer Urban Areas
| Speed Limit (km/h) | Maximum Spacing for Repeater Signs (km) |
| 10 | 0.5 |
| 20 | 0.5 |
| 30 | 0.75 |
| 40 (Heavy Vehicle Speed Zone) | 1 (Refer to Clause 2.2.5.2) |
| 50 | 1 |
| 60 | 1 |
| 70 | 1 |
| 80 | 1.5 |
| 90 | 1.5 |
| 100 | 3 |
| 110 | 4 |
(v) Repeater Signs in Rural Areas not subject to the built-up area speed limit
In rural areas, repeater signs shall be erected on the departure side (between 50 – 100 m on terminating legs, and between 100 – 200 m on continuing legs) of intersecting classified roads or any other roads carrying 75 vehicles per day or more, that intersect with the speed zoned road. Generally, these signs shall be spaced no closer than 0.5 km.
In more developed rural areas, the maximum spacing of repeater signs after consideration of signing at major intersections may vary between 5 and 10 km, depending upon the level of roadside development. In remote rural areas, repeater signing may be erected at 10 to 20 km spacing. In areas north of Meekatharra and Kalbarri and east of Norseman, repeater signs can be erected at greater intervals of about 25 to 50 km where there are low traffic volumes and long travel distances without a change of speed limit or intersecting roads.
f) Position and Number of Signs
(i) Speed Change Signs
Speed Change signs (R4-1) shall be doubled up and placed on the left hand and right hand side verges in the case of single carriageway roads and the left hand side verge and median side verge in the case of dual carriageway roads. The signs applying to a particular direction of travel shall not be staggered.
(ii) Repeater Signs
Repeater signs are single Speed Restriction signs (R4-1) mounted as follows:
- On single carriageway roads – on the left-hand side verge, refer to Figures 5(a) & (b).
- On dual carriageway roads with two or more lanes - on both the left-hand side verge and median side verge of the carriageway, staggered by approximately 100 m, Refer to Figure 5(e).
Figures 5(a) to 5(e) provide guidance on the location of speed zone signs in the vicinity of an intersection for a variety of scenarios.
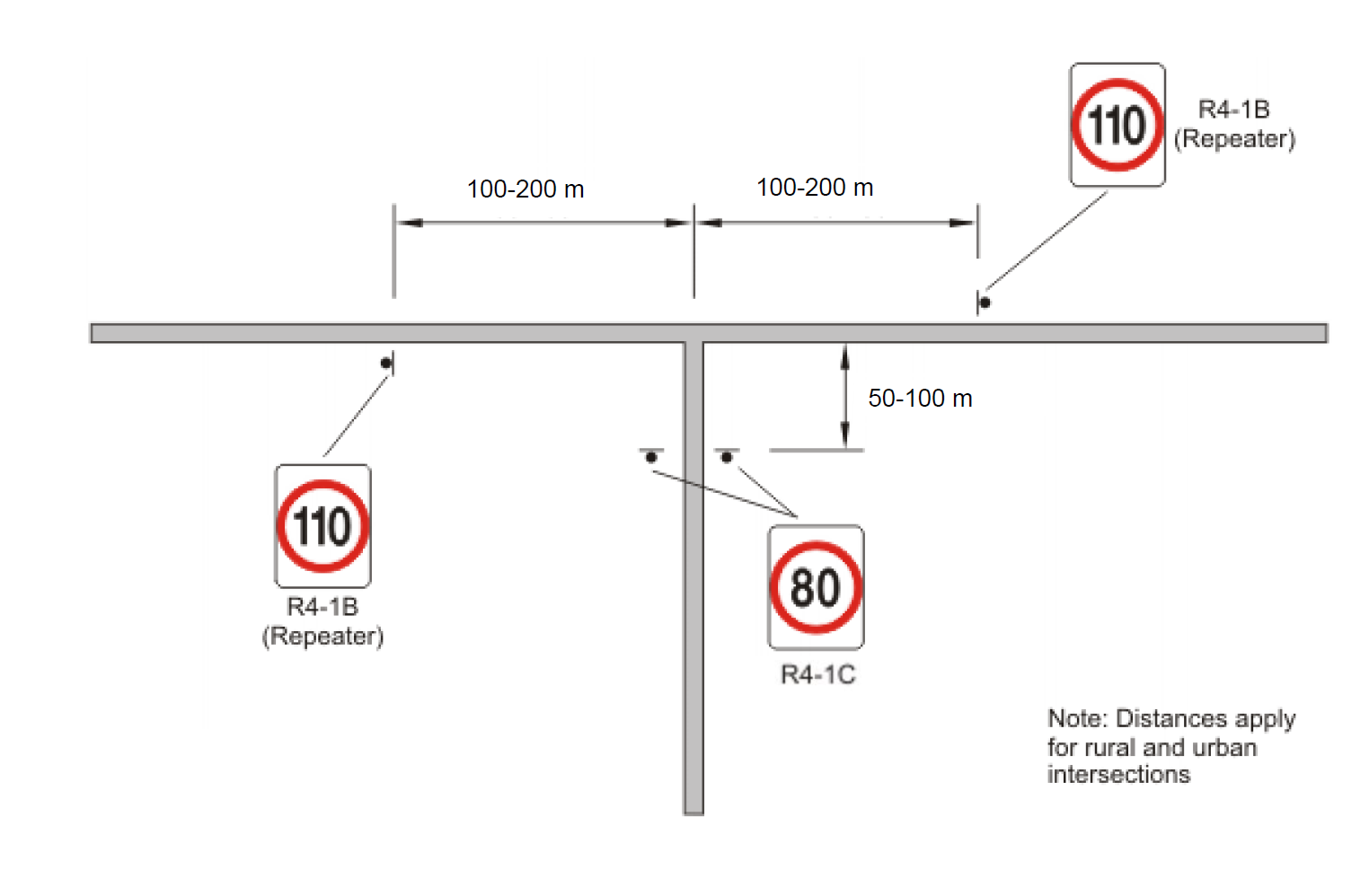
Figure 5(a): Location of Speed Zone Signs - Single Carriageway Roads, Unsignalised Intersection - Terminating Road Speed < Through Road Speed
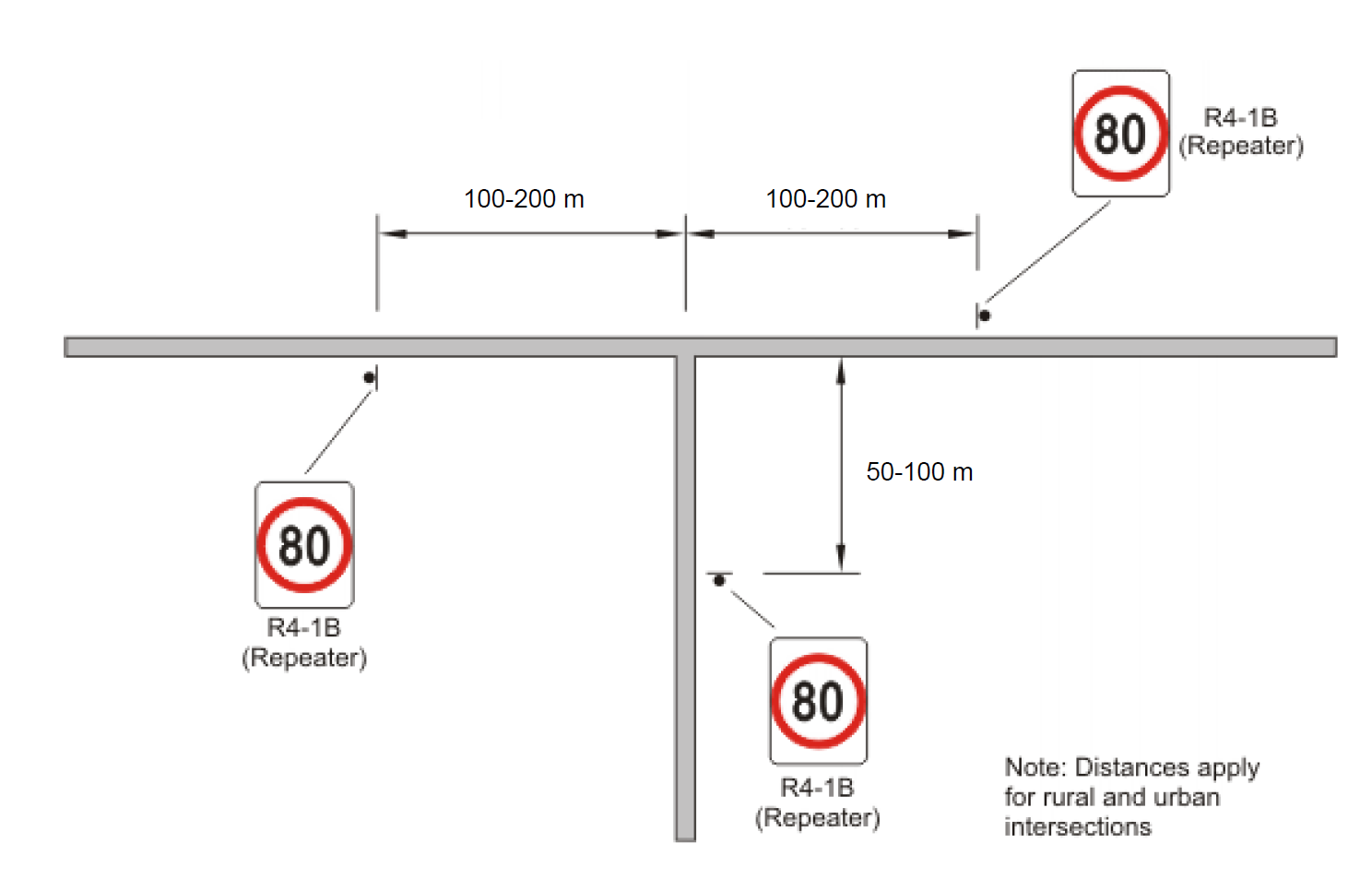
Figure 5(b): Location of Speed Zone Signs - Single Carriageway Roads, Unsignalised Intersection – Terminating Road Speed = Through Road Speed
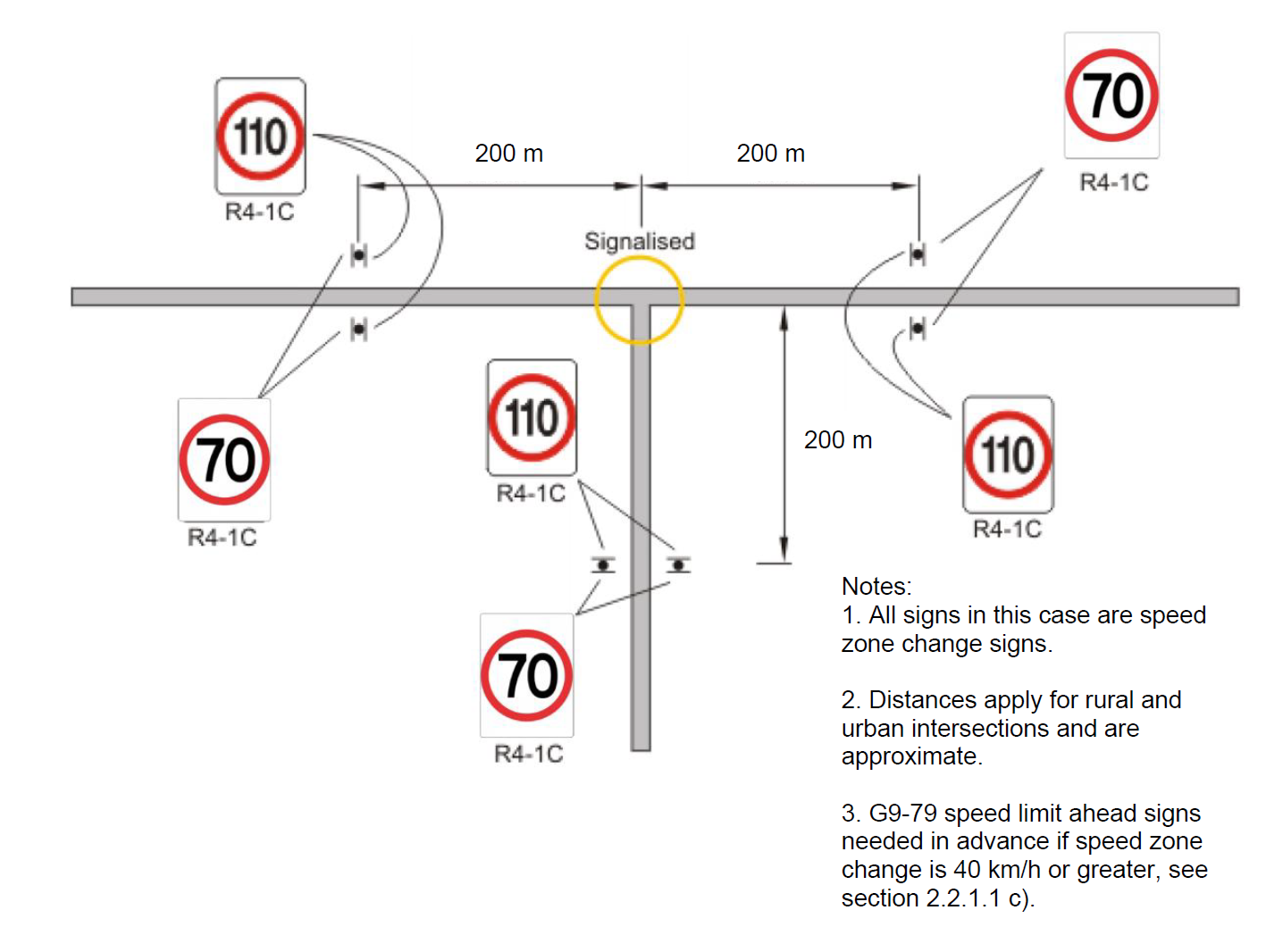
Figure 5(c): Location of Speed Zone Signs - Single Carriageway Roads, Signalised Intersection – Terminating Road Speed = Through Road Speed
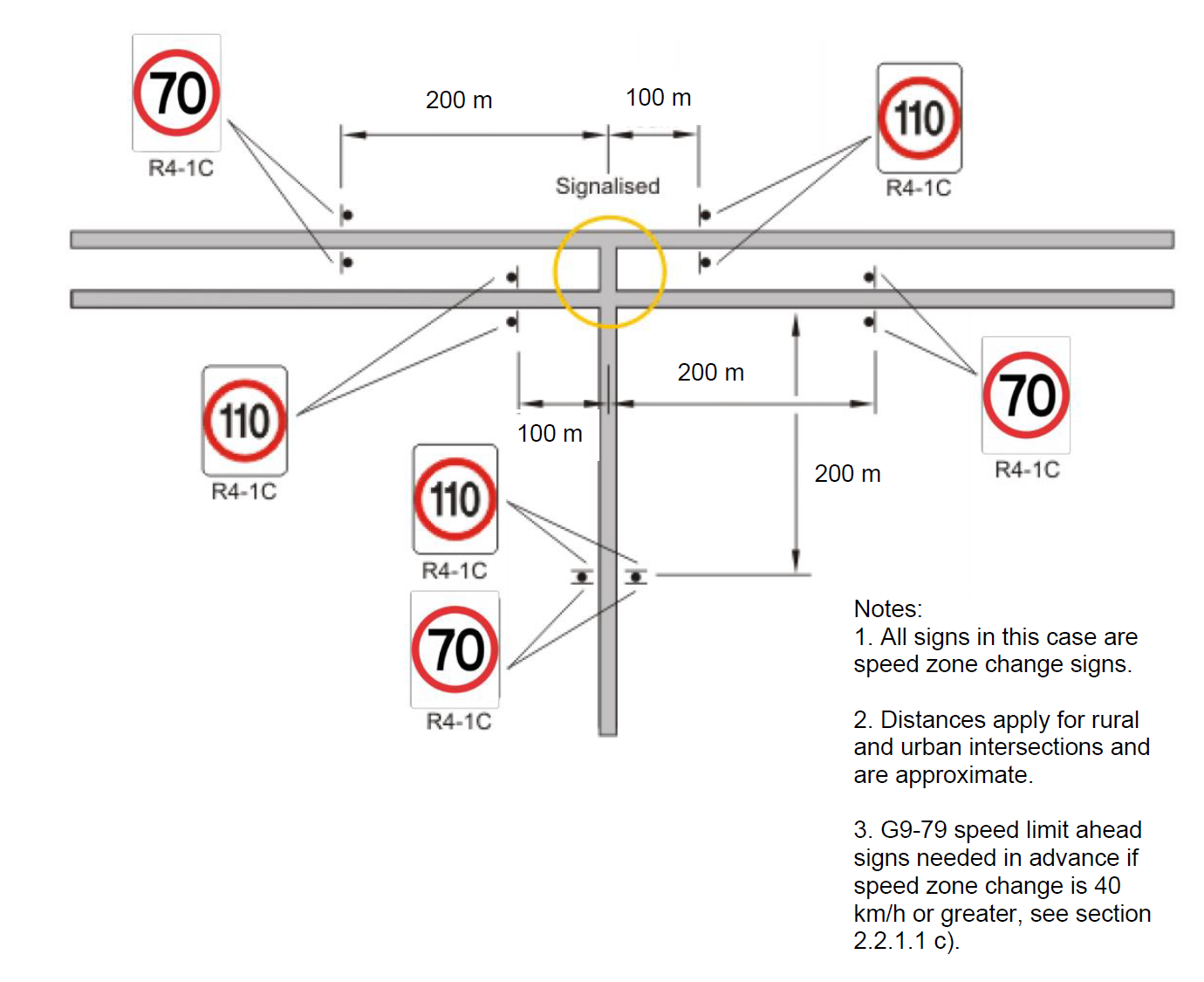
Figure 5(d): Location of Speed Zone Signs - Dual Carriageway on Main Road, Signalised Intersection – Terminating Road Speed = Through Road Speed
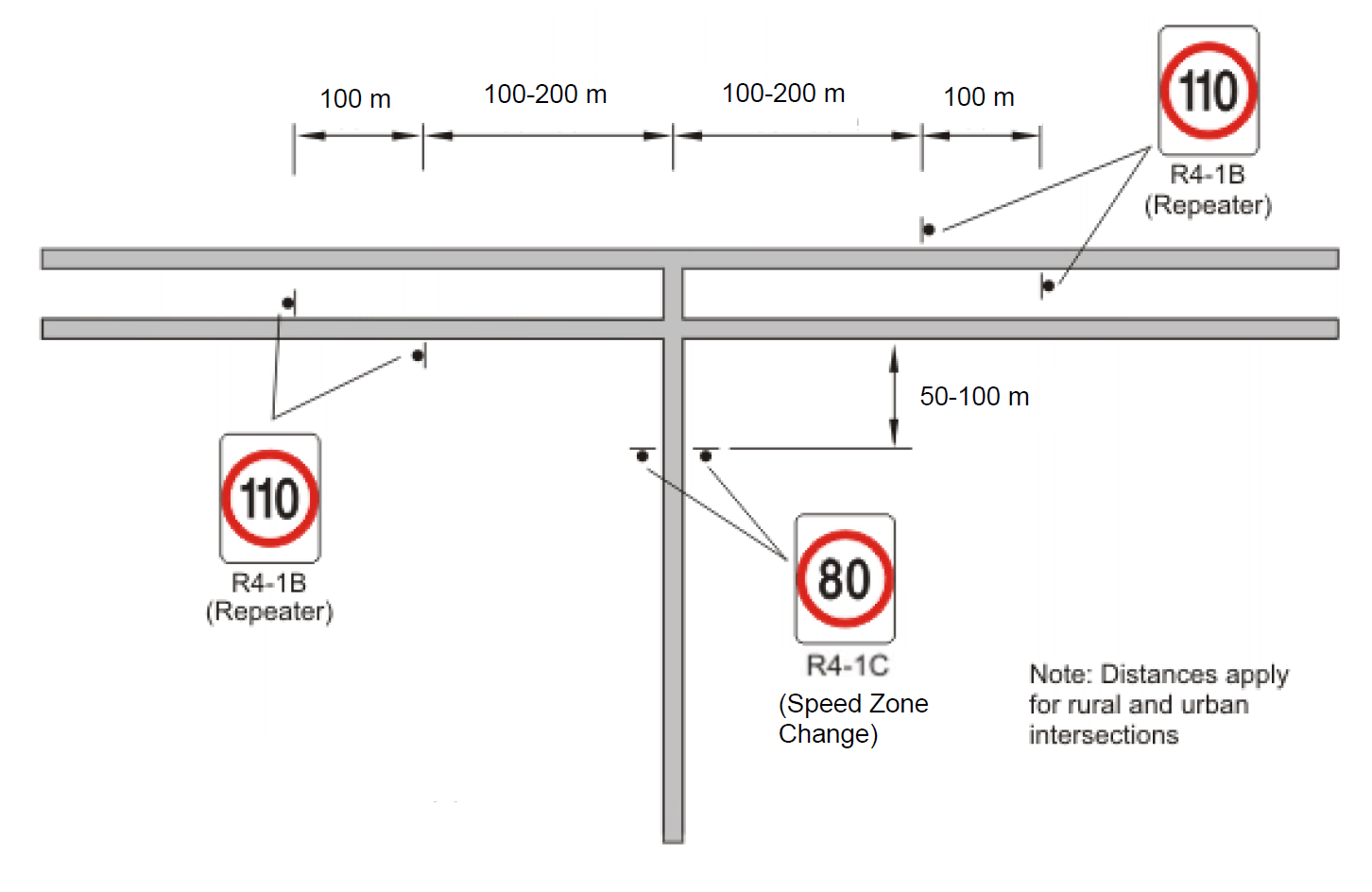
Figure 5(e): Location of Speed Zone Signs - Dual Carriageway (two or more lanes) on Main Road, Unsignalised Intersection
g) Freeway Exit and Entry Ramps
Advisory speed signs for freeway exit ramps shall be signed in accordance with AS 1742.2, clause 3.5(e).
Speed Restriction signs (R4-1) shall be installed as per Figures 7 and 8. These figures supersede Figures 3.1 and 3.2 of AS 1742.2 respectively. MR-GE-22 and MR-GE-23 signs are used in conjunction with R4-1 (Speed Limit) signs as described below in figure 6:
Figure 6
|
MR-GE-22 |
The MR-GE-22 (START OF FREEWAY) sign shall be used as a supplementary plate with a Speed Restriction sign (R4-1) to indicate the beginning of freeway conditions. The MR-GE-22 sign shall be used in lieu of the Australian Standard GE6-13 (START OF FREEWAY) sign |

MR-GE-23 |
The MR-GE-23 (END OF FREEWAY) sign shall be used as a supplementary plate with a Speed Restriction sign (R4-1) to indicate the end of freeway conditions. The MR-GE-23 sign shall be used in lieu of the Australian Standard GE6-11 (END OF FREEWAY) sign. |
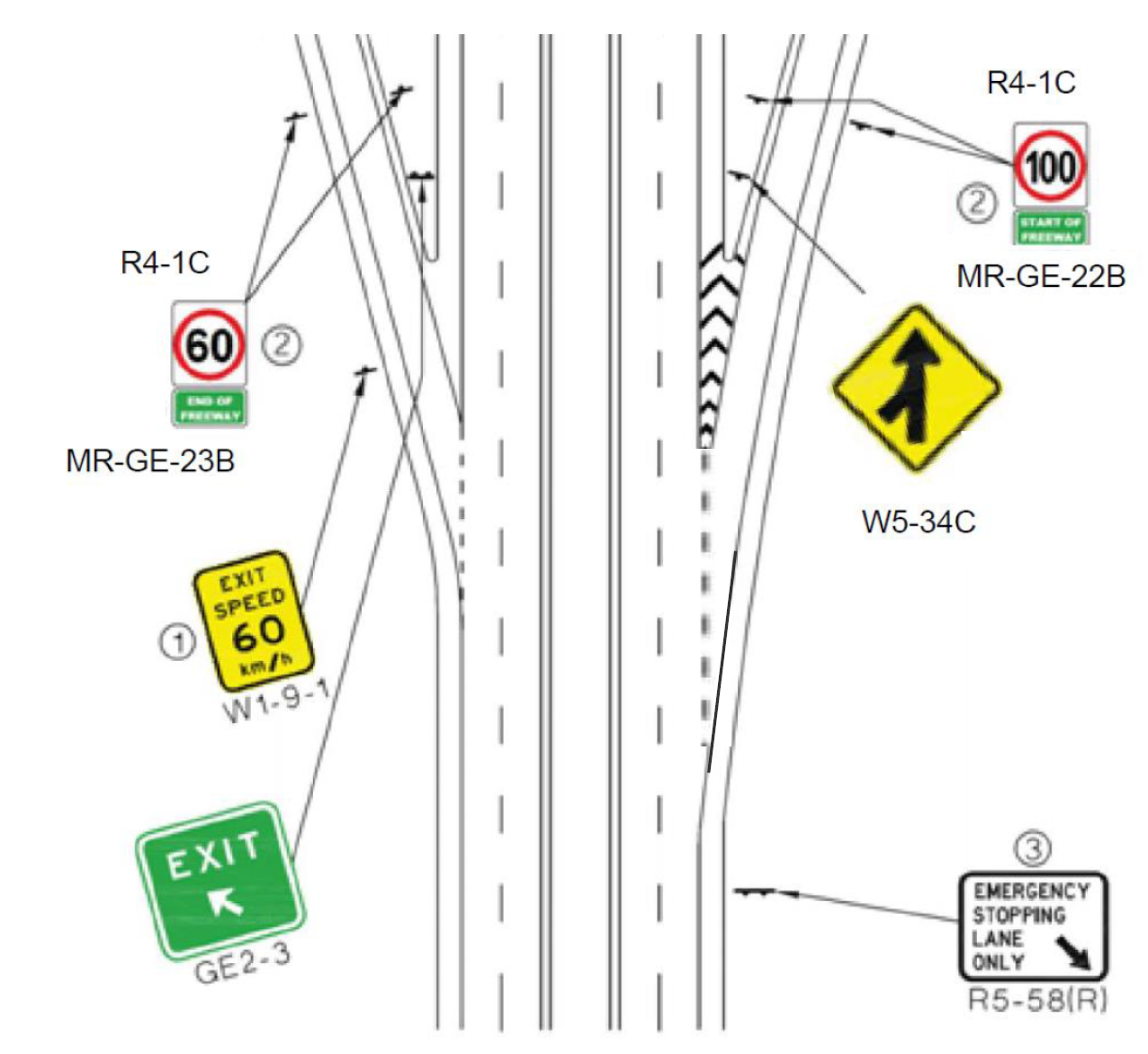
Notes:
- EXIT SPEED – used only if required [see Clause 2.2.1.2 g)].
- R4-1 signs (along with MR-GE-22 or MR-GE-23 supplementary plates, if used) shall be duplicated on both sides of the carriageway regardless of the number of lanes on the ramp at that point. The R4-1 sign with the speed zone for the road that the ramp joins should be located as far up the ramp near to the intersection to ensure drivers have maximum ramp distance to accelerate to the speed of the main through route that they will be about to join.
- Sign R5-58 is required near this location to prevent stopping on the freeway.
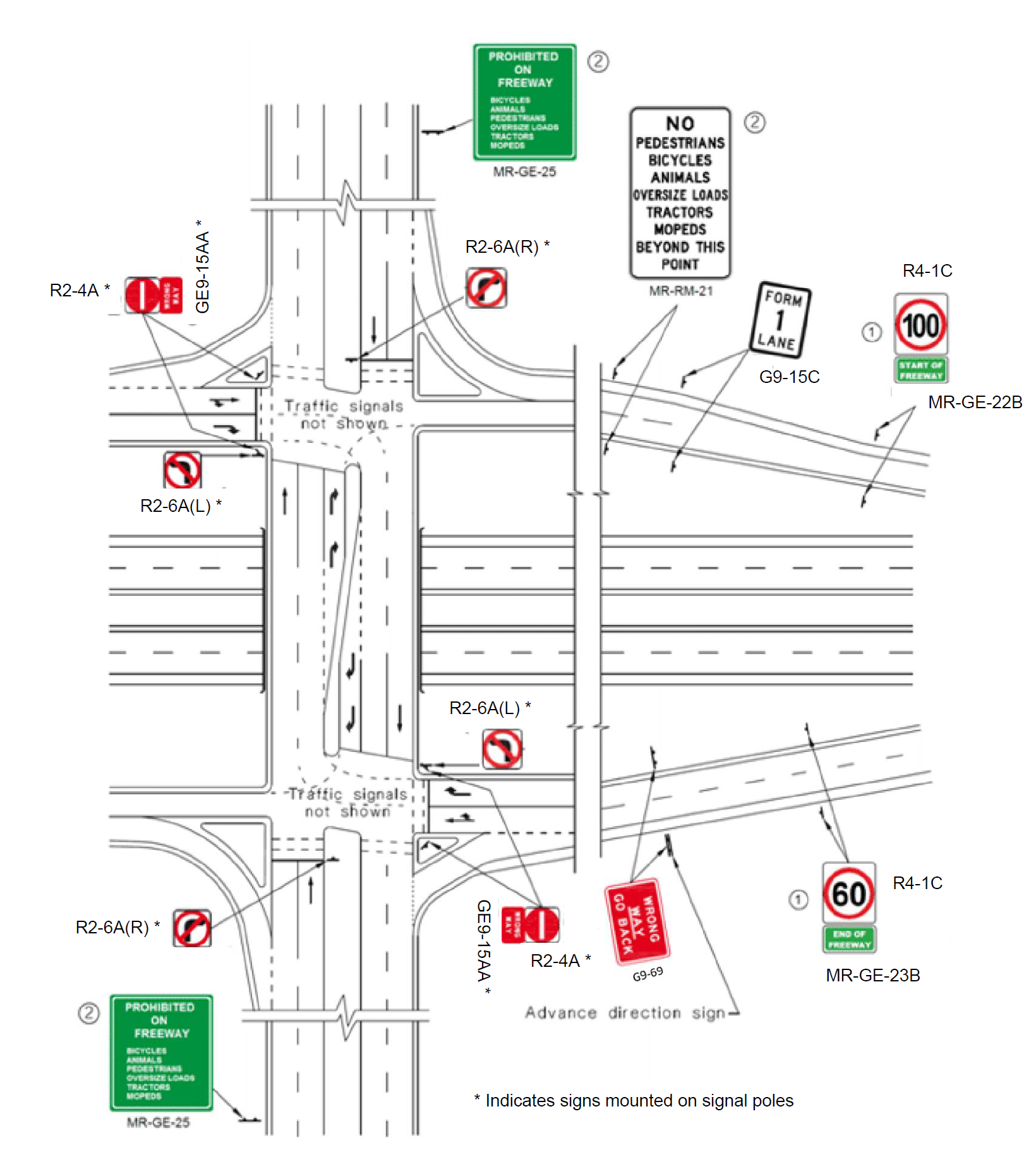
Notes:
- R4-1 signs (along with MR-GE-22 or MR-GE-23 supplementary plates, if used) shall be duplicated on both sides of the carriageway regardless of the number of lanes on the ramp at that point. R4-1 signs should be located to maximise distance for acceleration for drivers joining the main route.
- MR-RM-21 sign shall be duplicated on ramps with more than one lane. In addition, the advance information sign PROHIBITED ON FREEWAY (MR-GE-25), or PROHIBTED ON XXXX HWY (MR-GE-32), shall be erected on the approaches to the local road / freeway on-ramp intersection. Both MR-GE-25 (or MR-GE-32) and MR-RM-21 should be Modified based on prohibitions.
Figure 8: Typical Urban Cross Street with Ramp Treatment
h) Electronic and Variable Speed Zones
Where speed limits are required to vary either due to time of day or due to traffic volumes and conditions or due to events, electronic speed limit signs can be used to ensure drivers are aware of the prevailing speed limit. Electronic speed limit signs can be used for both linear speed limits and area speed limits such as School Zones. For further information on school zones refer to section 2.2.3 and the relevant section of the Speed Zoning - Policy and Application Guidelines.
Where electronic speed limit signs are used as part of a Lane Use Management System (LUMS) the appropriate information and size shall be used as described in the Main Roads document “Supplement to Victoria’s Managed Freeways Handbook for Lane Use Management and Variable Speed Limits. These devices need to be able to show multiple symbols and information at different times and the Main Roads electronic speed limit sign is not suitable as it can only show different speed limits. Further information for this type of sign can be found within Main Roads Smart Freeways documents available on the Main Roads website.
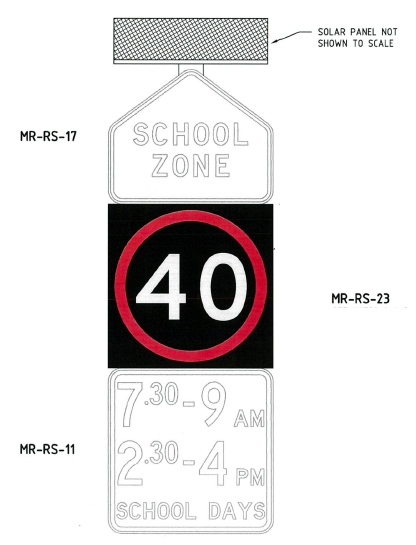
 MR-RS-23 |
The Electronic Speed Limit sign (MR-RS-23) shall be used when a variable speed limit, other than part of a LUMs, is controlled by an electronic sign. This sign is used as part of School Zones and, for example, at shopping strips that have variable speed limits. Standard Drawings 201031-0015 and associated standard drawing 201331-0010 demonstrate how this sign should be installed. Examples include South Western Highway at Byford Town site and Great Eastern Highway in Mundaring Town site. |
Figure 9.
i) Managed Freeways
Where a section of freeway (or other control of access highway) is to be managed as a “Smart Freeway” and have Lane Use Management System (LUMS) above each lane, to allow control of a variable speed limit, signs “When All Signs Blank” (MR-RS-24) and signs “When Sign Blank” (MR-RS-25) shall be used as appropriate for the number of lanes and associated electronic signs, refer figure 10. All signs / sign blank signs (MR-RS-24 or MR-RS-25) shall be used at all locations where overhead signs or freestanding signs on the edge of the road are used. The “When All Signs Blank” sign shall be doubled up on both sides of the road / carriageway. Refer to figure 11. Both signs, MR-RS-24 and MR-RS-25, are a specified size as demonstrated on the standard drawings.
| Sign | Location |
|
MR-RS-24 |
The MR-RS-24 sign is used to assist with degraded operation of VSL signs. It is installed on the gantry leg where LUMS or VSL signs are installed. If the gantry is a cantilever structure then the sign may also be installed on the verge opposite the gantry leg, if appropriate. Signs to be installed on every gantry at the beginning of an area with no shoulder and at the start of any areas where the maximum speed limit changes. |
|
MR-GE-22B
MR-RS-25 |
The MR-RS-25 sign is used to assist with degraded operation of VSL signs. It is installed on entry ramps where the ramp enters a LUMS or VSL environment - located beneath the Start of Freeway sign and VSL sign. Where a VSL sign is used in a Smart Freeway application, other than as part of a LUMS on an entry ramp, the MR-GE-22B sign is omitted, see figure 12. The MR-RS-25 sign will show a lower speed limit than the normal free flow speed limit shown on the VSL Sign, in most cases 20 km/h lower. |
Figure 10.
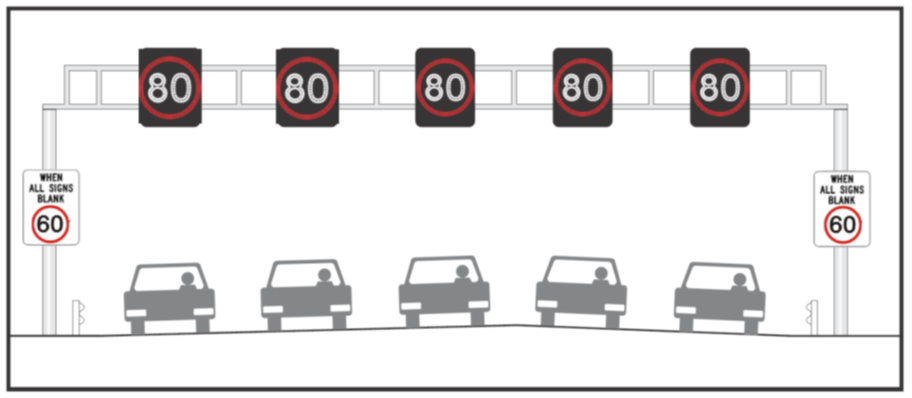
Figure 11. When All Signs Blank signs (MR-RS-24) shown on gantry accompanying LUMS electronic signs. 80 km/h speed limit shown with 60 km/h speed limit when electronic signs are blank.
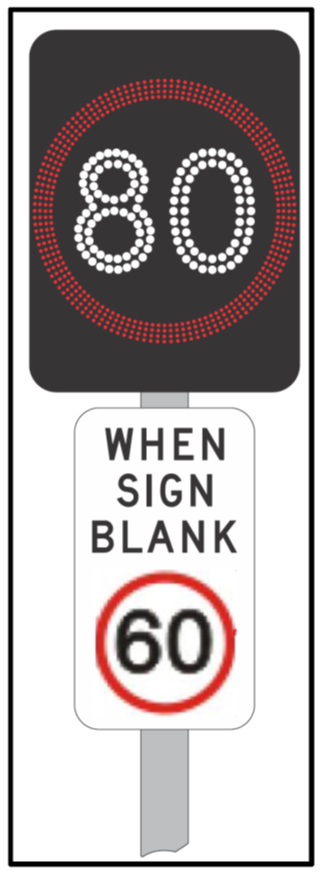
Figure 12. When Sign Blank sign (MR-RS-25) shown underneath Electronic Speed Limit sign.
2.2.1.3 Pavement Markings
a) Longitudinal
For two-lane, two-way roads, it is desirable that a dividing line or barrier line is provided on a section of road that is speed zoned.
b) Numerals
Numerals may be installed where considered appropriate to supplement speed limit signs on the approaches to a road section in accordance with requirements set out below and in AS1742.4. Where provided, the following shall apply:
- For a speed limit decrease at the end of a significant length of road with a speed limit of 100 km/h or higher,
- For exit ramps from Freeway and Freeway standard roads advance warning of a change in speed limit may be applied, with the numerals of the approaching speed limit supplemented with the word AHEAD, where horizontal or vertical alignments create limited approach sight lines of the change.
- The location of the pavement marking is on a straight section of road.
- Markings shall be 5 m long where the approaching traffic is in a speed zone of 90 km/h or more.
- Markings shall be 2.5 m long where the approaching traffic is in a speed zone of 80 km/h or less.
- The numerals shall be installed in each marked lane.
- Pavement markings shall not be installed on a curve.
2.2.2 Area Speed Zones
Area speed zones shall have appropriate signs erected at every entry and exit point in accordance with the clauses 2.2.2.1 to 2.2.2.4.
2.2.2.1 Entry signs
Speed Limit AREA signs (R4-10) shall be placed on both sides of the road to face traffic entering the zone. They shall be positioned approximately 30 to 50 m from any intersection to enable them to be readily seen by drivers after they have turned from the intersecting street (Refer to Figure 14).
2.2.2.2 Exit Signs
The exit signs required for speed zone areas depend on the type of roadway (continuing or terminating) and the speed limit of the road after passing the exit sign.
With reference to Figure 14, if after the end of the speed zone area the road returns to a default speed such as the Built-Up Area speed limit then END speed limit AREA signs (R4-11B) shall be used. If the speed zone area changes to a non-default speed limit then the new speed limit sign (R4-1B) with the smaller END speed limit AREA sign (R4-13) shall be used.
|
R4-11 |
For terminating roads, END Speed Limit AREA signs (R4-11) shall be placed on both sides of the road, back-to-back with the Speed Limit AREA signs (R4-10). For continuing roads, where the speed limit of the continuing road is the default speed limit, END Speed Limit AREA signs (R4-11) shall be placed on both sides of the road, back-to-back with the Speed Limit AREA signs (R4-10). Refer to figure 14 for example of use. |
 R4-13 above R4-1 |
For continuing roads, where the speed limit of the continuing road is not the default speed limit, END Speed Limit AREA signs (R4-13), together with Speed Limit signs (R4-1) shall be placed on both sides of the road, back-to-back with Speed Limit AREA signs (R4-10). |
|
|
Previously the END Speed Limit AREA signs were (MR-RS-20) and used with the Speed Limit signs (R4-1). New installations should utilise the Australian Standard sign (R4-13) as shown above. |
Figure 13.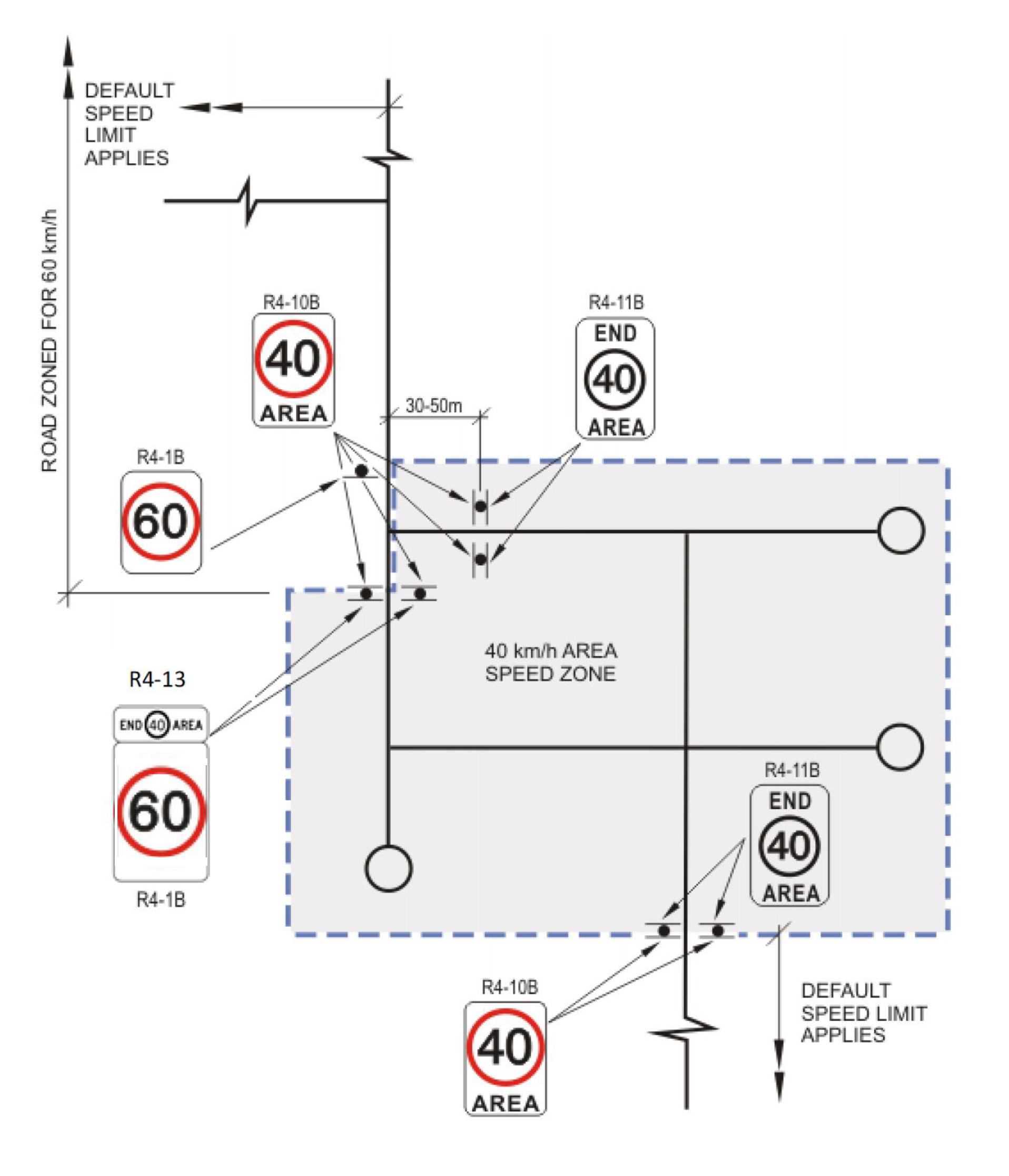
Figure 14: Application of Area Speed Zone Signs
2.2.2.3 Repeater Signs
Area Speed signs (R4-10) are to be used as repeater speed limit signs and shall be installed within the speed limited area at approximately 0.5 km intervals on each continuous street that is longer than 1 km.
2.2.2.4 Sizes of Area Speed Zone Signs
For sizes of Area Speed Zone signs, refer to Section 2.2.1.2 d).
2.2.3 School ZonesSchool Zones can be applied to particular roads in the vicinity of pre-primary, primary and secondary schools to reduce traffic speeds at times of the day when school children are likely to be present on or about these roads. Refer to Speed Zoning - Policy and Application Guidelines section 5.4.
2.2.3.1 Speed Limits
All School Zones shall have a Posted Speed Limit of 40 km/h (except for roads already zoned at a lower Posted Speed value for example a Safe Active Street location).
2.2.3.2 Times of Operation
To ensure state-wide uniformity the following times of operation are used on School Zone signs. These standard times allow for the variations in individual school start and finish times refer table 5.
Table 5 - School Zone Times
| Location | Hours of operation |
| Gascoyne and Pilbara | 07:30 – 9:00 a.m. and 2:00 to 3:30 p.m. |
| Kimberley | 07:00 – 8.30 a.m. and 2:00 to 3:30 p.m. |
| Carnarvon | 07:30 – 9:00 a.m. and 2:00 to 4:00 p.m. |
| Rest of WA | 07:30 – 9:00 a.m. and 2:30 to 4:00 p.m. |
All times of operation within a town or city shall be consistent.
2.2.3.3 Length of School Zones
School zones should extend at least the full length of the school frontage. Generally, school zones extend about 50 m beyond the school boundary to effectively cover children crossing in the vicinity of the school.
The minimum length of a school zone along the main school frontage should generally be not less than:
- 200 metres where the school zone speed limit is 40 km/h.
Where a school zone is also installed on a secondary school frontage road, the length of the school zone may be considerably less than that specified for the main frontage.
The actual lengths of school zones should be determined from the needs of the individual school, having regard for the type of road, traffic volume, traffic speed, visibility and road conditions. Where possible, the school zone on the main school frontage should be installed such that the point at which most students enter and leave the school is centred within the school zone.
The existence and location of school crossing facilities (such as children's crossings, marked pedestrian crossings, or pedestrian refuges) should be taken into account in determining the length of the school zone. The school zone should extend over a length sufficient to include any such facilities in the immediate proximity of the school.
Where two schools are nearby, both independently satisfying the selection criteria, one continuous school zone serving both schools shall be applied if the separation distance between separate school zones is 300 m or less.
2.2.3.4 School Zone Signs
The start of a school zone shall be defined by a "School Zone" sign indicating the reduced speed limit and the times and days of operation. In Western Australia, the preferred practice is that the Australian Standard signs R4-8 (school zone), R4-1 (speed restriction) and R9-1-2 (times of operation) are combined into a single "School Zone" sign. Figure 17 illustrates a typical school zone sign layout. It should be noted that "Enhanced School Zone" signs shall only be used at the start of the zone along those roads which front onto the school site. "Enhanced School Zone" signs have a five-sided fluorescent yellow green "hat", which may be part of the sign (MR-RS-15B and MR-RS-16B), or which may be attached as a separate plate (MR-RS-17) to a School Zone sign (MR-RS-7B, MR-RS-8B, MR-RS-9B or MR-RS14B).
Figure 15
|
MR-RS-7B |
The MR-RS-7B (School Zone – all regions except Northern Regions) sign is used to sign a school zone speed limit of 40 km/h in all areas of Western Australia other than the Northern Region (Gascoyne, Pilbara and Kimberley Regions). This sign may be used at the start of a school zone on roads which terminate on roads which front onto the school site. This sign may also be used on its own as a repeater sign within the school zone. This sign may be used in conjunction with a MR-RS-17 "Supplementary Plate to Enhance School Zone Signs" at the start of a school zone on those roads which front onto the school site although sign MR-RS-15B is preferred. |
|
MR-RS-8B |
The MR-RS-8B (School Zone – Gascoyne and Pilbara) sign is used to sign a school zone speed limit of 40 km/h in Gascoyne and Pilbara Regions other than in the town of Carnarvon. This sign may be used at the start of a school zone on roads which terminate on roads which front onto the school site. This sign may also be used on its own as a repeater sign within the school zone. This sign may be used in conjunction with a MR-RS-17 "Supplementary Plate to Enhance School Zone Signs" at the start of a school zone on those roads which front onto the school site although sign MR-RS-16B is preferred. |
|
MR-RS-9B |
The MR-RS-9B (School Zone – Kimberley) sign is used to sign the start of a school zone speed limit of 40 km/h on those roads which front onto the school site in the Kimberley Region. This sign may be used at the start of a school zone on roads which terminate on roads which front onto the school site. This sign may also be used on its own as a repeater sign within the school zone. This sign may be used in conjunction with a MR-RS-17 "Supplementary Plate to Enhance School Zone Signs" at the start of a school zone on those roads which front onto the school site although sign MR-RS-29B is preferred. |
|
MR-RS-14B |
The MR-RS-14B (School Zone - Carnarvon) sign is used in the town of Carnarvon only to sign a school zone speed limit of 40 km/h. This sign may be used at the start of a school zone on roads which terminate on roads which front onto the school site. This sign may also be used on its own as a repeater sign within the school zone. This sign may be used in conjunction with a MR-RS-17 "Supplementary Plate to Enhance School Zone Signs" at the start of a school zone on those roads which front onto the school site although sign MR-RS-30B is preferred. |
 MR-RS-30B |
The MR-RS-30B (Enhanced School Zone – Carnarvon) sign is used to sign the start of a school zone speed limit of 40 km/h on those roads which front onto the school site in the town of Carnarvon. |
|
|
The MR-RS-29B (Enhanced School Zone – Kimberley) sign is used to sign the start of a school zone speed limit of 40 km/h on those roads which front onto the school site in the Kimberley Region. |
|
|
The MR-RS-15B (Enhanced School Zone – all regions except Northern Regions) sign is used to sign the start of a school zone speed limit of 40 km/h on those roads which front onto the school site in all areas of Western Australia except Northern Regions. |

MR-RS-16B |
The MR-RS-16B (Enhanced School Zone – Gascoyne and Pilbara Regions) sign is used to sign the start of a school zone speed limit of 40 km/h on those roads which front onto the school site in all Gascoyne and Pilbara Regions of Western Australia |

MR-RS-17 |
Updated MR-RS-17 (Supplementary Plate to Enhance School Zone Signs) sign may be used with the School Zone signs MR-RS-7B, MR-RS-8B, MR-RS-9 and MR-RS-14B to sign the start of a school zone speed limit on those roads which front onto the school site. The sign is normally used to retrospectively convert an existing "School Zone" sign to an "Enhanced School Zone" sign. This sign may also be used for maintenance purposes where the fluorescent yellow green "school zone" panel has faded in a MR-RS-15B or MR-RS-16B sign. |
|
R4-9 |
The "End School Zone" sign (R4-9) is a regulatory sign and shall be used to identify the end of a school zone. Where the speed limit beyond the school zone is subject to a speed zone greater or less than the general built-up area or rural limit, the "End School Zone" sign shall be installed in conjunction with the appropriate speed restriction sign. Where the speed limit beyond the school zone is the same as the general built-up area or rural limit, the "End School Zone" shall be installed on its own. On two-lane, two-way roadways, the "End School Zone" sign is generally installed back-to-back on the same post as the "School Zone Sign" (refer to Figure 17). It should be noted that the "End of School Zone" sign (MR-RS-13) is no longer used, although it is still supported under the Road Traffic Code 2000. |
|
MR-RS-11 |
The MR-RS-11 (School Zone Times except Northern Regions) sign demonstrates the time when the school zone is in operation for all areas in Western Australia except the Northern regions. This sign is used as part of the combination of signs to form the Electronic School Zone sign. |

MR-RS-27 |
The MR-RS-27 (School Zone Times – Kimberley Region) sign demonstrates the time when the school zone is in operation for the Kimberley Region. This sign is used as part of the combination of signs to form the Electronic School Zone sign. |
|
MR-RS-12 |
The MR-RS-12 (School Zone Times – Gascoyne and Pilbara Regions) sign demonstrates the time when the school zone is in operation for the Gascoyne and Pilbara Regions. This sign is used as part of the combination of signs to form the Electronic School Zone sign. |
 MR-RS-26 |
The MR-RS-26 (School Zone Times – Carnarvon) sign demonstrates the time when the school zone is in operation within the Town of Carnarvon. This sign is used as part of the combination of signs to form the Electronic School Zone sign. |
With reference to Figure 17, the following installation principles apply to School Zones:
- For two-lane two-way roads leading directly past the school, the start of a School Zone shall have "Enhanced School Zone" signs on both sides of the road. The end of the school zone shall have "End School Zone" signs on both sides of the road, fixed back to back on a single post with the "Enhanced School Zone" signs.
- For two-lane, two-way roads with a raised refuge island, or for four-lane divided roads with a narrow median (≤ 2 m) leading directly past the school, the start of a School Zone shall have "Enhanced School Zone" signs on the left-hand side and the central median. The end of a School Zone shall have "End School Zone" signs on the left-hand side and the central median. The signs in the central median shall be fixed back to back on a single post.
- For four-lane divided roads with a wide median (> 2 m) leading directly past the school, the start of a School Zone should have "Enhanced School Zone" signs on the left hand side and the central median. The end of a School Zone should have "End School Zone" signs on the left-hand side and the central median. All signs shall be mounted on their own posts.
- For roads joining onto roads leading directly past the school, the start of a School Zone is indicated by a School Zone sign installed on the left-hand side of the road. The End of School Zone sign is attached back to back on the same post.
- Signs are not required on loop roads that have both ends within the school zone and which fronts onto the school site or cul-de-sacs less than 200 m long.
- School Zone signs may be repeated to reassure drivers that they are still within the school zone if the lengths of the frontage roads are greater than 300 m.
- Size 'B' School Zone signs shall be used in all cases, unless only one size is available.
- Although not shown in figure 17, school zone ahead warning signs should be used as described in figure 2 in section 2.2.1.1 b).
Electronic School Zone Signs
|
MR-RS-17, MR-RS-23 and MR-RS-11 |
The Electronic School Zone sign is a combination of other signs as shown with the MR-RS-23 sign replacing the R4-1 sign. This sign is used in place of the enhanced school zone sign utilising the MR-RS-17 “top hat” sign along with the time sign MR-RS-11 or relevant time sign if within Northern Regions. |
Figure 16.
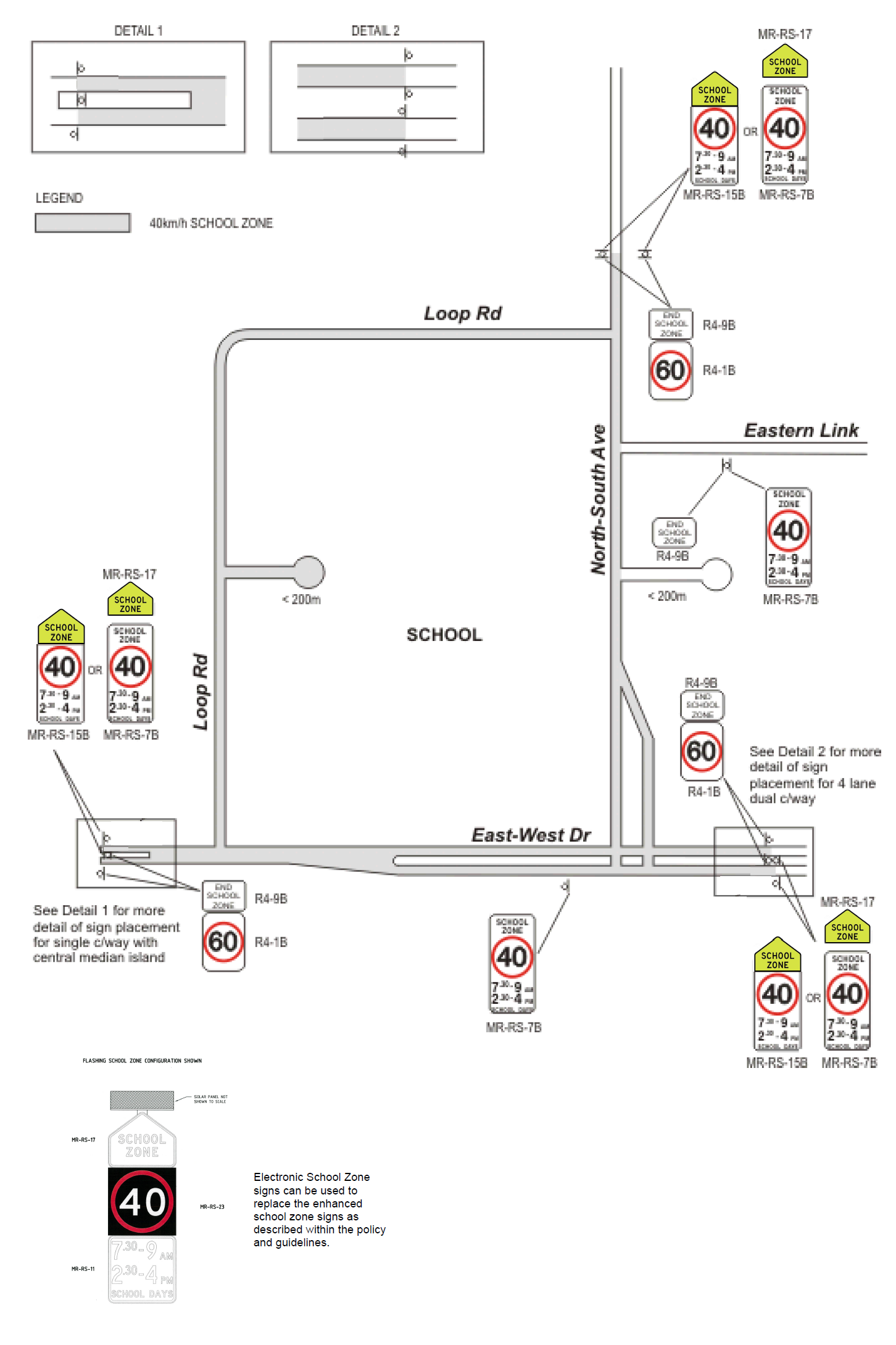
Figure 17: Typical School Zone Sign Layout
a) Signing Practices that are no longer current
The following signing practices are no longer current, although there may still be installations employing these practices on the road network. Any such installations should be replaced with signs complying with current practice when these signs become due for replacement under the maintenance agreements.
Where the preferred practice of combining the individual Australian Standard signs R4-8 (school zone), R4-1 (speed restriction) and R9-1-2 (times of operation) into a single "school zone" sign indicated in section 2.2.3.4, is not adhered to, the following has been applied.
Figure 18

Not to be used |
The MR-RS-11 sign has been used in the past in lieu of the Australian Standard "Times of Operation" sign R9-1-2 and in conjunction with the Australian Standard "School Zone" sign (R4-8B) and Speed Restriction sign (R4-1B) to indicate the times a school zone speed restriction applies in all regions of Western Australia, other than the Northern Regions (Gascoyne, Pilbara and Kimberley regions). Current preferred practice is to use the Main Roads signs MR-RS-7B. Check table 5 for school zones times in different regions and locations. |
|
Not to be used |
The MR-RS-12 sign has been used in the past in lieu of the Australian Standard "Times of Operation" sign R9-1-2 and in conjunction with the Australian Standard "School Zone" sign (R4-8B) and Speed Restriction sign (R4-1B) to indicate the times a school zone speed restriction applies in all Gascoyne and Pilbara Regions of Western Australia. Current preferred practice is to use the Main Roads sign MR-RS-8B. Check table 5 for school zones times in different regions and locations. |
|
Not to be used |
The "Direction Arrow" sign (MR-RS-10) was used in the past in conjunction with signs MR-RS-7B, MR-RS-8B, MR-RS-9B and MR-RS-14B to indicate to drivers approaching a School Zone from a side road that the road they are joining is zoned as a "School Zone". The sign was positioned opposite the T-junction, facing terminating traffic. This practice is no longer necessary (Figure 17 refers) and is being phased out. |
2.2.3.5 Road Markings
Previously some school zones met warrants for “40” pavement markings when entering the zone. These pavement markings are now no longer supported and should not be reinstated after resurfacing or installed at new school zone locations.2.2.4.1 General
A Shared Zone is a length of carriageway or a network of roads in an area on which vehicular traffic must give way to pedestrians, where the road environment has been adapted for low vehicle speeds and on which the speed limit is either 10 km/h or 20 km/h as shown on the signs.
2.2.4.2 Signs
Signs shall be installed in accordance with AS1742.4 Section 3.1.10 except as described within this section. The speed limit numerals within Shared Zone sign R4-4 can be altered to display either 10 or 20. Where a shared zone ends and the speed limit is not the default limit then the End Shared Zone sign to MR-RS-31 shall be used above the R4-1 speed zone sign to end the shared zone. Refer to figure 19.
Figure 19

R4-4 |
The SHARED ZONE sign to R4-4 is used to commence a shared zone. The speed limit numerals can be either 10 or 20 as required. This sign has only one size. |

MR-RS-31 above R4-1 |
Where a shared zone ends and the new speed limit is not the default speed limit, END SHARED ZONE signs (MR-RS-31), can be placed above the Speed Limit signs (R4-1). This combination would replace the R4-5 End Shared Zone sign as found within AS1742.4 section 3.1.10. |
2.2.4.3 Pedestrian Mall
A pedestrian mall is equivalent to a shared zone with a 10 km/h speed limit. Most vehicles are prohibited from entering a pedestrian mall with certain types of vehicles, as stated within the RTC, allowed to enter. Signs to MR-RP-2 and MR-RP-6, see figure 20, create the pedestrian mall and the subsequent requirements for a 10 km/h speed limit as stated in the RTC. Sign MR-RP-2 displays times when service vehicles cannot enter the pedestrian mall and sign MR-RP-6 does not show any time restrictions for service vehicles.
Figure 20

MR-RP-2 |
Sign MR-RP-2 (Pedestrian Mall) shall be erected at the entrance to a pedestrian mall. The regulatory sign creates a right of way for pedestrians and limits the speed of vehicles to a maximum of 10 km/h and the type of vehicle that may enter the mall. A time when service vehicles cannot enter the pedestrian mall is displayed. |

MR-RP-6 |
Sign MR-RP-6 (Pedestrian Mall) shall be erected at the entrance to a pedestrian mall. The regulatory sign creates a right of way for pedestrians and limits speed of vehicles to a maximum of 10 km/h and the type of vehicle that may enter the pedestrian mall. |
2.2.5 Heavy Vehicle Speed Zones
2.2.5.1 General
The RTC allows the implementation of Heavy Vehicle Speed Zones, restricting the speed of heavy vehicles to the speed limit indicated by numbers shown on the 'heavy vehicle speed zone' sign. The RTC defines a heavy vehicle as 'a vehicle, other than a bus, that has, or together with any attached trailer and its load has, a Gross Combined Mass (GCM) that is 22.5 t or more'. In the context of this definition, the speed restriction would also apply to a vehicle having a Gross Vehicle Mass (GVM) of 22.5 t or more.
The preferred speed zone restriction for heavy vehicles is 40 km/h, but this may be varied depending upon the situation. Conditions applicable for the installation of heavy vehicle speed zone signs are given in Section 5.6 of the Speed Zoning - Policy and Application Guidelines.2.2.5.2 Signs
Figure 21
|
MR-RS-18 |
Sign MR-RS-18 (Heavy Vehicle Speed Zone) shall be erected at the start of a length of carriageway to which a heavy vehicle speed zone applies. |
|
MR-RS-19 |
Sign MR-RS-19 (End of Heavy Vehicle Speed Zone) shall be erected at the end of a length of carriageway to which a heavy vehicle speed zone applies. |
|
R4-1B & MR-RA-21 |
Signs R4-1B and MR-RA-21 shall be used as repeater signs for Heavy Vehicle Speed Zones and shall be located at approximately 1.0 km intervals, or 50 m past any repeater signs indicating the speed limit for other vehicles |
2.2.6 Advisory Speed Signing
Advisory speed signing shall be limited to horizontal and vertical curves (including LATM devices) on sealed roads. These are signed with curve warning and advisory speed signs in accordance with AS 1742.2 Section 4.4, unless otherwise directed in this guideline. Advisory speed signing for freeway exit ramps is to be in accordance with AS1742.2 clause 3.5 (e).
Wherever possible it is preferable to determine advisory speeds by field assessment. For existing roads, the determination of advisory speeds for substandard curves shall be undertaken in accordance with the methods given in Appendix F of AS 1742.2. Where there is a need to determine safe operating (advisory) speed from design drawings, the following formula shall be used, and the advisory speed shall be set at the nearest 5km/h increment below the calculated safe operating (advisory) speed.
V2 = R x 127 x (e + f)
Therefore,
![]()
Where:
V = Speed in kilometres per hour.
R = Radius of curve
e = superelevation in m/m
f = absolute maximum side friction factor.
If not known, the side friction factor should be determined by referral to the MRWA Supplement to Austroads Guide to Road Design (AGRD) Part 3 table 7.5.
Where there is a series of more than two closely spaced horizontal curves, some or all of which are substandard, the symbolic "Winding Road" sign (W1-5) shall be used at the beginning of the series of curves. The winding road sign used shall indicate the direction of the first substandard curve and the advisory speed sign shall indicate the advisory speed of the slowest curve. However, if the series of curves extends over a distance of one kilometre or more and the slowest curve is more than 10 km/h slower than the others, the slowest curve is to be signed separately.
Section 3.2 of AS1742.4 shall apply with respect to the conflict between speed limits and advisory speed signs.
If the crash level on a section of speed zoned road with advisory speed signing becomes greater than the network average for that type of road, then that road section may be speed zoned at a lower value.
Advisory Speed signs shall not be used in conjunction with Crossroad (W2-1), T-junction (W2-3 and W2-14), Roundabout (W2-7), Side Road Junction (W2-4, W2-8 and W2-13) or Modified Intersection Warning (W9 series) signs, where a driver may be required to give way to other vehicles.
2.2.6.1 Advisory Signs
Figure 22

MR-WM-57 |
Sign MR-WM-57 (REMEMBER 50 IN BUILT-UP AREAS) is an advisory warning sign that can only be erected on a road that meets the Built-Up Area definition and has the BUA speed limit. The sign can only be installed if criteria in section 5 of the Speed Zoning - Policy and Application Guidelines have been met. This sign was previously a temporary sign intended to be used in 2001 when the BUA speed limit changed from 60 km/h to 50 km/h. |
2.2.7 Temporary Signing
Following the introduction of a new speed limit on an existing road temporary signs can be used to inform road users of the changes.
“New Speed Limit Ahead” (MR-TAW-25) can be used when a speed limit has been changed. Refer to figure 23.
“New 50 speed limit” (MR-TAW-40) can be used when an existing speed limit has been changed to the Built-Up Area Default of 50 km/h and no other signing would normally be shown. Refer to figure 23.
Figure 23

MR-TAW-25 |
Sign MR-TAW-25 (New Speed Limit Ahead) can be erected in advance of the start of a length of carriageway to which a new speed limit now applies. The new speed limit can be higher or lower than the existing limit. This sign shall only be installed for a temporary time period of 3 to 6 months in duration. This sign is not used in advance of new school zones or other speed zones that change, shared zones and Safe Active Streets. |

MR-TAW-40 |
Sign MR-TAW-40 (New 50 km/h Built Up Area default speed limit) shall be erected where an existing speed limit has changed to become the Built Up Area (BUA) default speed limit of 50 km/h. This sign ensures that for a short time period following the speed zone change drivers are aware that the speed limit has altered. In the absence of this temporary sign there would be no visual cue to drivers of the change in speed limit except the absence of the previous speed limit sign. This sign shall only be installed for a temporary time period of 3 to 6 months in duration. |














 MR-RS-15B
MR-RS-15B